
Renaissance Art
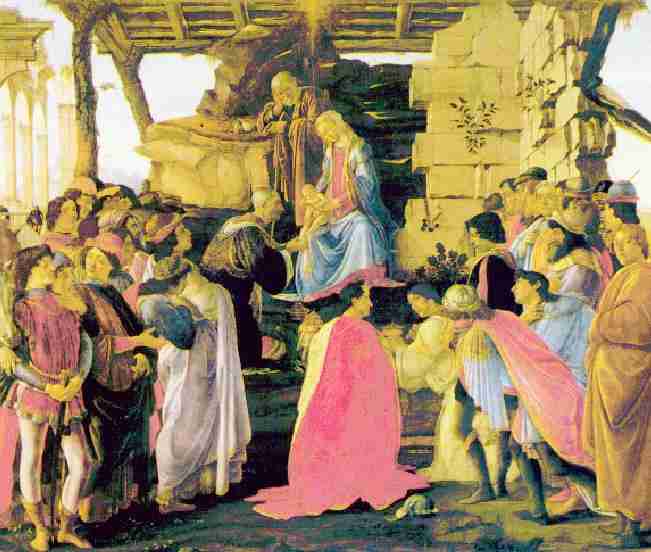
Figure 1.--This Biblical scene, "The adoration of the Magi" ws painted by Botticelli probably about 1475. It is a familiar Biblical nativity scene. Note that the characters in the scene are outfitted in contemorary Italian Renaissance clothing, not Biblical eraclothing.
|
The European Renaissance began in Italy. It involved fundamental changes in the way individuals viewed their world. A central element of the Renaissance was the rediscovery of ancient world of Greece and Rome. The ancient classics of philosophy, literature, and science inspired the development of empirical methods to persue studies in these fields. As Europeans became increasingly aware of classical knowledge some thinkers like Galileo began to build on that knowldge actual observation and study of the natural world, even conceiving experiments to test his theories. It is art, however, that is the most vissible indication of the changing outlook of Europeans. The focus on the natural world caused many artists to move away from the Medieval focus on God to an increasing concern with the natural world and more precise depictions of that world. The horrors of the plague had caused many to question their faith in the 14th century, another factor in undermining a God-centered world. As a result, the themes of Renaissance artists are less and less devote to the glory of God and increasingly to secular themes. Many artists now not only paint Biblical scenes but Greek and Roman history and mythology are depicted. Later in the Renaissance, artists will begin painting genre scenes of contemporary life. The increasingly sophisticated artistic techniques permit artists to create amazingly realistic depictions. The role of the artist also changes in the Renaissance. The Medievl artist was a craftsman whose name, especially in the early Medieval era. was rarely applied to his creations. His task was to Glorify God along guidelines clearly established by the Church. The Renaissance artist was a very diufferent indidividual. He was much more than a craftman. He was a creator. And he was viewed very differently than the mere artisan artists were viewed in the Medieval era. The Renaissance artist was greatly respected in a world still dominated by the airistoracy. Both the airistocracy and the Church and later in the Mefdieval era wealthy merchants began respecting the artist not only for his technical prowess, but also for his creative powers and imagination--in fact a new development in Western art. The artist was seen as an individual whose personal aesthetic expression was of importance. One fascinating aspect of Renaissance art is that early artists often painted Biblical and classical scenes, but depicted the subjects in contemporary Renaissance clothing.
The European Renaissance began in Italy. It involved fundamental changes in the way individuals viewed their world. A central element of the Renaissance was the rediscovery of ancient world of Greece and Rome. The ancient classics of philosophy, literature, and science inspired the development of empirical methods to persue studies in these fields. As Europeans became increasingly aware of classical knowledge some thinkers like Galileo began to build on that knowldge actual observation and study of the natural world, even conceiving experiments to test his theories.
Visual Indication
It is art, however, that is the most vissible indication of the changing outlook of Europeans. The focus on the natural world caused many artists to move away from the Medieval focus on God to an increasing concern with the natural world and more precise depictions of that world. The horrors of the plague had caused many to question their faith in the 14th century, another factor in undermining a God-centered world.
Themes
The changing world view of Europeans was reflected un their art and the themes depicted. The themes of Renaissance artists are less and less devote to the glory of God and increasingly to secular themes. Many artists now not only paint Biblical scenes but Greek and Roman history and mythology are depicted. Later in the Renaissance, artists will begin painting genre scenes of contemporary life.
Technology and Technique
The increasingly sophisticated artistic techniques permit artists to create amazingly realistic depictions. Art and science are often conceived as polar opposites. In fact the art of the Renaissance was in part due to important scientific and mathematical advances. Italian painters developed magestic artistic techniques during the Renaissance that gradually spread north over the Alps. The techniques included: geometric perspective, chiaroscuro, and naturalistic depictions.
Role of the Artist
The role of the artist also changes in the Renaissance. The Medievl artist was a craftsman whose name, especially in the early Medieval era. was rarely applied to his creations. His task was to Glorify God along guidelines clearly established by the Church. The Renaissance artist was a very diufferent indidividual. He was much more than a craftman. He was a creator. And he was viewed very differently than the mere artisan artists were viewed in the Medieval era. The Renaissance artist was greatly respected in a world still dominated by the airistoracy. Both the airistocracy and the Church and later in the Mefdieval era wealthy merchants began respecting the artist not only for his technical prowess, but also for his creative powers and imagination--in fact a new development in Western art. The artist was seen as an individual whose personal aesthetic expression was of importance.
Individual Artists
Filippo Brunelleschi invented one-point perspective, leading to major innovations in Italian art and architecture. Leonardo da Vinci's inventive mind and spectacular art fuels the Rennaisance. The leading German artist of th enaissance was Albrecht Dürer.
Clothing Depictions
One fascinating aspect of Renaissance art is that early artists often painted Biblical and classical scenes, but depicted the subjects in contemporary Renaissance clothing. Much of our knowledge of contemporary fashion and clothing comes from the art of the era.
HBC

Navigate the Boys' Historical Clothing artistic pages:
[Return to the Main Renaissance page]
[Return to the Main artistic page]
[Chronologies]
[Individuals]
[National]
[Styles]
Navigate the Boys' Historical Clothing Web Site:
[Introduction]
[Activities]
[Biographies]
[Chronology]
[Clothing styles]
[Countries]
[Topics]
[Bibliographies]
[Contributions]
[FAQs]
[Glossaries]
[Satellite sites]
[Tools]
[Boys' Clothing Home]
Created: August 18, 2003
Last updated: 5:04 AM 1/22/2006



